Header Files In C
InC language, header files contain a set of predefined standard library functions. The .h is the extension of the header files in C and we request to use a header file in our program by including it with the C preprocessing directive “#include”. C language has numerous libraries that include predefined functions to make programming easier.
C++ Language also offers its users a variety of functions, one of which is included in header files. In C++, all the header files may or may not end with the “.h” extension.
It offers the features like library functions, data types, macros, etc by importing them into the program with the help of a preprocessor directive “#include”. These preprocessor directives are used to instruct the compiler that these files need to be processed before compilation.
 |
| Header files in C |
Syntax of Header Files in C/C++
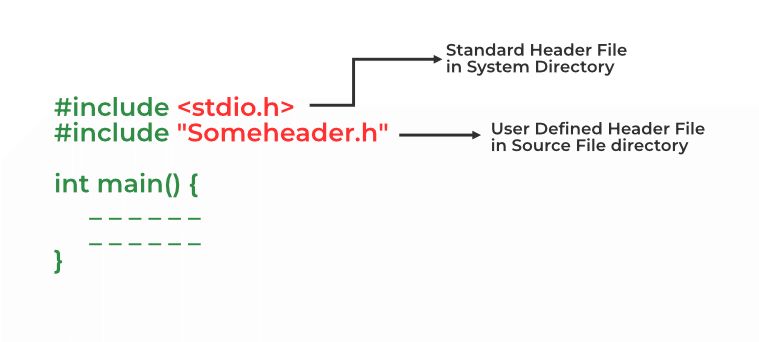
We can include header files in C by using one of the given two syntaxes whether it is a pre-defined or user-defined header file.
#include <filename.h> // for files in system/default directory
or
#include "filename.h" // for files in same directory as source fileThe “#include” preprocessor directs the compiler that the header file needs to be processed before compilation and includes all the necessary data types and function definitions.
Example
- C
- C++
Printf() is the function in stdio.h header fileTypes of Header Files
There are two types of header files in C and C++:
- Standard / Pre-existing header files
- Non-Standard / User-defined header files
1. Standard Header Files in C and their Uses
Standard header files contain the libraries defined in the ISO standard of the C programming language. They are stored in the default directory of the compiler and are present in all the C compilers from any vendor.
There are 31 standard header files in the latest version of C language. Following is the list of some commonly used header files in C:
Header File | Description |
|---|---|
| <assert.h> | It contains information for adding diagnostics that aid program debugging. |
| <errorno.h> | It is used to perform error handling operations like errno(), strerror(), perror(), etc. |
| <float.h> | It contains a set of various platform-dependent constants related to floating point values. These constants are proposed by ANSI C. They make programs more portable. Some examples of constants included in this header file are- e(exponent), b(base/radix), etc. |
| <math.h> | It is used to perform mathematical operations like sqrt(), log2(), pow(), etc. |
| <signal.h> | It is used to perform signal handling functions like signal() and raise(). |
| <stdarg.h> | It is used to perform standard argument functions like va_start() and va_arg(). It is also used to indicate start of the variable-length argument list and to fetch the arguments from the variable-length argument list in the program respectively. |
| <ctype.h> | It contains function prototypes for functions that test characters for certain properties, and also function prototypes for functions that can be used to convert uppercase letters to lowercase letters and vice versa. |
| <stdio.h> | It is used to perform input and output operations using functions like scanf(), printf(), etc. |
| <setjump.h> | It contains standard utility functions like malloc(), realloc(), etc. It contains function prototypes for functions that allow bypassing of the usual function call and return sequence. |
| <string.h> | It is used to perform various functionalities related to string manipulation like strlen(), strcmp(), strcpy(), size(), etc. |
| <limits.h> | It determines the various properties of the various variable types. The macros defined in this header limits the values of various variable types like char, int, and long. These limits specify that a variable cannot store any value beyond these limits, for example, an unsigned character can store up to a maximum value of 255. |
| <time.h> | It is used to perform functions related to date() and time() like setdate() and getdate(). It is also used to modify the system date and get the CPU time respectively. |
| <stddef.h> | It contains common type definitions used by C for performing calculations. |
| <locale.h> | It contains function prototypes and other information that enables a program to be modified for the current locale on which it’s running. It enables the computer system to handle different conventions for expressing data such as times, dates, or large numbers throughout the world. |
Comments
Post a Comment